fixed tree functions and added times function
This commit is contained in:
parent
bbb2aabeb8
commit
13afac33a4
3 changed files with 247 additions and 78 deletions
65
docs/api.md
65
docs/api.md
|
|
@ -878,6 +878,71 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
|
||||
drone.box( blocks.torch + ':' + Drone.PLAYER_TORCH_FACING[drone.dir]);
|
||||
|
||||
Drone times Method
|
||||
==================
|
||||
The times() method makes building multiple copies of buildings easy. It's possible to create rows or grids of buildings without resorting to `for` or `while` loops.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
* numTimes (optional - default 2) : The number of times you want to repeat the preceding statements.
|
||||
|
||||
Example
|
||||
-------
|
||||
Say you want to do the same thing over and over. You have a couple of options...
|
||||
|
||||
* You can use a for loop...
|
||||
|
||||
d = new Drone(); for (var i =0;i < 4; i++){ d.cottage().right(8); }
|
||||
|
||||
While this will fit on the in-game prompt, it's awkward. You need to
|
||||
declare a new Drone object first, then write a for loop to create the
|
||||
4 cottages. It's also error prone, even the `for` loop is too much
|
||||
syntax for what should really be simple.
|
||||
|
||||
* You can use a while loop...
|
||||
|
||||
d = new Drone(); var i=4; while (i--){ d.cottage().right(8); }
|
||||
|
||||
... which is slightly shorter but still too much syntax. Each of the
|
||||
above statements is fine for creating a 1-dimensional array of
|
||||
structures. But what if you want to create a 2-dimensional or
|
||||
3-dimensional array of structures? Enter the `times()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
The `times()` method lets you repeat commands in a chain any number of
|
||||
times. So to create 4 cottages in a row you would use the following
|
||||
statement...
|
||||
|
||||
cottage().right(8).times(4);
|
||||
|
||||
...which will build a cottage, then move right 8 blocks, then do it
|
||||
again 4 times over so that at the end you will have 4 cottages in a
|
||||
row. What's more the `times()` method can be called more than once in
|
||||
a chain. So if you wanted to create a *grid* of 20 houses ( 4 x 5 ),
|
||||
you would do so using the following statement...
|
||||
|
||||
cottage().right(8).times(4).fwd(8).left(32).times(5);
|
||||
|
||||
... breaking it down...
|
||||
|
||||
1. The first 3 calls in the chain ( `cottage()`, `right(8)`,
|
||||
`times(4)` ) build a single row of 4 cottages.
|
||||
|
||||
2. The last 3 calls in the chain ( `fwd(8)`, `left(32)`, `times(5)` )
|
||||
move the drone forward 8 then left 32 blocks (4 x 8) to return to
|
||||
the original x coordinate, then everything in the chain is
|
||||
repeated again 5 times so that in the end, we have a grid of 20
|
||||
cottages, 4 x 5. Normally this would require a nested loop but
|
||||
the `times()` method does away with the need for loops when
|
||||
repeating builds.
|
||||
|
||||
Another example: This statement creates a row of trees 2 by 3 ...
|
||||
|
||||
oak().right(10).times(2).left(20).fwd(10).times(3)
|
||||
|
||||
... You can see the results below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Drone.sphere() method
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
Creates a sphere.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
BIN
docs/img/times-trees.png
Normal file
BIN
docs/img/times-trees.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After 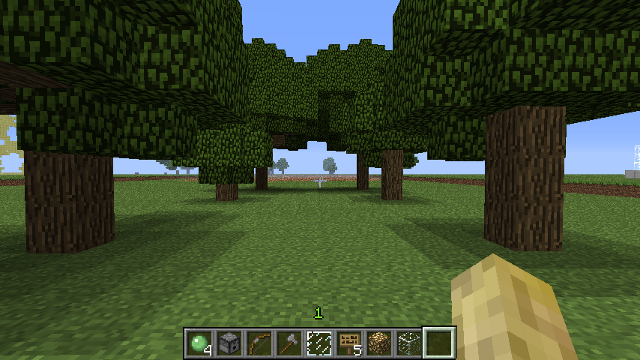
(image error) Size: 299 KiB |
|
|
@ -678,6 +678,7 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
(function(){
|
||||
Drone = function(x,y,z,dir,world)
|
||||
{
|
||||
this.record = false;
|
||||
var usePlayerCoords = false;
|
||||
var playerPos = getPlayerPos();
|
||||
if (typeof x == "undefined"){
|
||||
|
|
@ -722,14 +723,131 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
this.fwd(3);
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.chkpt('start');
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.chkpt = function(name){
|
||||
this._checkpoints[name] = {x:this.x,y:this.y,z:this.z,dir:this.dir};
|
||||
this.record = true;
|
||||
this.history = [];
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype.move = function()
|
||||
//
|
||||
// add custom methods to the Drone object using this function
|
||||
//
|
||||
Drone.extend = function(name, func)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Drone.prototype[name] = func;
|
||||
Drone.prototype['_' + name] = func;
|
||||
Drone.prototype[name] = function(){
|
||||
if (this.record)
|
||||
this.history.push([name,arguments]);
|
||||
var oldVal = this.record;
|
||||
this.record = false;
|
||||
this['_' + name].apply(this,arguments);
|
||||
this.record = oldVal;
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
global[name] = function(){
|
||||
var result = new Drone();
|
||||
result[name].apply(result,arguments);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
/**************************************************************************
|
||||
Drone times Method
|
||||
==================
|
||||
The times() method makes building multiple copies of buildings easy. It's possible to create rows or grids of buildings without resorting to `for` or `while` loops.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
* numTimes (optional - default 2) : The number of times you want to repeat the preceding statements.
|
||||
|
||||
Example
|
||||
-------
|
||||
Say you want to do the same thing over and over. You have a couple of options...
|
||||
|
||||
* You can use a for loop...
|
||||
|
||||
d = new Drone(); for (var i =0;i < 4; i++){ d.cottage().right(8); }
|
||||
|
||||
While this will fit on the in-game prompt, it's awkward. You need to
|
||||
declare a new Drone object first, then write a for loop to create the
|
||||
4 cottages. It's also error prone, even the `for` loop is too much
|
||||
syntax for what should really be simple.
|
||||
|
||||
* You can use a while loop...
|
||||
|
||||
d = new Drone(); var i=4; while (i--){ d.cottage().right(8); }
|
||||
|
||||
... which is slightly shorter but still too much syntax. Each of the
|
||||
above statements is fine for creating a 1-dimensional array of
|
||||
structures. But what if you want to create a 2-dimensional or
|
||||
3-dimensional array of structures? Enter the `times()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
The `times()` method lets you repeat commands in a chain any number of
|
||||
times. So to create 4 cottages in a row you would use the following
|
||||
statement...
|
||||
|
||||
cottage().right(8).times(4);
|
||||
|
||||
...which will build a cottage, then move right 8 blocks, then do it
|
||||
again 4 times over so that at the end you will have 4 cottages in a
|
||||
row. What's more the `times()` method can be called more than once in
|
||||
a chain. So if you wanted to create a *grid* of 20 houses ( 4 x 5 ),
|
||||
you would do so using the following statement...
|
||||
|
||||
cottage().right(8).times(4).fwd(8).left(32).times(5);
|
||||
|
||||
... breaking it down...
|
||||
|
||||
1. The first 3 calls in the chain ( `cottage()`, `right(8)`,
|
||||
`times(4)` ) build a single row of 4 cottages.
|
||||
|
||||
2. The last 3 calls in the chain ( `fwd(8)`, `left(32)`, `times(5)` )
|
||||
move the drone forward 8 then left 32 blocks (4 x 8) to return to
|
||||
the original x coordinate, then everything in the chain is
|
||||
repeated again 5 times so that in the end, we have a grid of 20
|
||||
cottages, 4 x 5. Normally this would require a nested loop but
|
||||
the `times()` method does away with the need for loops when
|
||||
repeating builds.
|
||||
|
||||
Another example: This statement creates a row of trees 2 by 3 ...
|
||||
|
||||
oak().right(10).times(2).left(20).fwd(10).times(3)
|
||||
|
||||
... You can see the results below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
***/
|
||||
Drone.prototype.times = function(numTimes,commands)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (typeof numTimes == "undefined")
|
||||
numTimes = 2;
|
||||
if (typeof commands == "undefined")
|
||||
commands = this.history.concat();
|
||||
|
||||
this.history = [['times',[numTimes+1,commands]]];
|
||||
var oldVal = this.record;
|
||||
this.record = false;
|
||||
for (var j = 1; j < numTimes; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (var i = 0;i < commands.length; i++){
|
||||
var command = commands[i];
|
||||
var methodName = command[0];
|
||||
var args = command[1];
|
||||
print ("command=" + JSON.stringify(command) + ",methodName=" + methodName);
|
||||
this[methodName].apply(this,args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
this.record = oldVal;
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype._checkpoints = {};
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.extend('chkpt',function(name){
|
||||
this._checkpoints[name] = {x:this.x,y:this.y,z:this.z,dir:this.dir};
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.extend('move', function() {
|
||||
if (arguments[0] instanceof org.bukkit.Location){
|
||||
this.x = arguments[0].x;
|
||||
this.y = arguments[0].y;
|
||||
|
|
@ -753,53 +871,48 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
this.z = arguments[2];
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
this.y = arguments[1];
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
case 1:n
|
||||
this.x = arguments[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype._checkpoints = {};
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype.turn = function(n){
|
||||
Drone.extend('turn',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
this.dir += n;
|
||||
this.dir %=4;
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.right = function(n){
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('right',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
return _movements[this.dir].right(this,n);
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.left = function(n){
|
||||
_movements[this.dir].right(this,n);
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('left',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
return _movements[this.dir].left(this,n);
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.fwd = function(n){
|
||||
_movements[this.dir].left(this,n);
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('fwd',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
return _movements[this.dir].fwd(this,n);
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.back = function(n){
|
||||
_movements[this.dir].fwd(this,n);
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('back',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
return _movements[this.dir].back(this,n);
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.up = function(n){
|
||||
_movements[this.dir].back(this,n);
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('up',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
this.y+= n;
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.down = function(n){
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('down',function(n){
|
||||
if (typeof n == "undefined")
|
||||
n = 1;
|
||||
this.y-= n;
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
//
|
||||
// position
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
|
@ -809,7 +922,7 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
//
|
||||
// building
|
||||
//
|
||||
Drone.prototype.sign = function(message,block){
|
||||
Drone.extend('sign',function(message,block){
|
||||
if (message.constructor == Array){
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
message = [message];
|
||||
|
|
@ -832,8 +945,7 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
if (block == 68){
|
||||
this.fwd();
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.prototype.cuboida = function(/* Array */ blocks,w,h,d){
|
||||
var properBlocks = [];
|
||||
var len = blocks.length;
|
||||
|
|
@ -904,7 +1016,6 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype.cuboid = function(block,w,h,d){
|
||||
|
||||
var bm = this._getBlockIdAndMeta(block);
|
||||
return this.cuboidX(bm[0],bm[1], w,h,d);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
|
@ -922,26 +1033,26 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
|
||||
return this.move('start_point');
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.door = function(door){
|
||||
Drone.extend('door',function(door){
|
||||
if (typeof door == "undefined"){
|
||||
door = 64;
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
door = 71;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this.cuboid(door+':' + this.dir).up().cuboid(door+':8').down();
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.door2 = function(door){
|
||||
this.cuboid(door+':' + this.dir).up().cuboid(door+':8').down();
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('door2',function(door){
|
||||
if (typeof door == "undefined"){
|
||||
door = 64;
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
door = 71;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this
|
||||
this
|
||||
.box(door+':' + this.dir).up()
|
||||
.box(door+':8').right()
|
||||
.box(door+':9').down()
|
||||
.box(door+':' + this.dir).left();
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
// player dirs: 0 = east, 1 = south, 2 = west, 3 = north
|
||||
// block dirs: 0 = east, 1 = west, 2 = south , 3 = north
|
||||
// sign dirs: 5 = east, 3 = south, 4 = west, 2 = north
|
||||
|
|
@ -949,18 +1060,6 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
// for blocks 68 (wall signs) 65 (ladders) 61,62 (furnaces) 23 (dispenser) and 54 (chest)
|
||||
Drone.PLAYER_SIGN_FACING = [4,2,5,3];
|
||||
Drone.PLAYER_TORCH_FACING = [2,4,1,3];
|
||||
//
|
||||
// add custom methods to the Drone object using this function
|
||||
//
|
||||
Drone.extend = function(name, func)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Drone.prototype[name] = func;
|
||||
global[name] = function(){
|
||||
var result = new Drone();
|
||||
result[name].apply(result,arguments);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
var _getWorld = function(){
|
||||
var pl = org.bukkit.entity.Player;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1050,11 +1149,11 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
this.fwd(f).up(f).cuboid(se,w).down(f).back(f);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.prism0 = _prism0;
|
||||
Drone.prototype.prism = _prism;
|
||||
Drone.prototype.box = Drone.prototype.cuboid;
|
||||
Drone.prototype.box0 = Drone.prototype.cuboid0;
|
||||
Drone.prototype.boxa = Drone.prototype.cuboida;
|
||||
Drone.extend('prism0',_prism0);
|
||||
Drone.extend('prism',_prism);
|
||||
Drone.extend('box',Drone.prototype.cuboid);
|
||||
Drone.extend('box0',Drone.prototype.cuboid0);
|
||||
Drone.extend('boxa',Drone.prototype.cuboida);
|
||||
//
|
||||
// show the Drone's position and direction
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
|
@ -1292,11 +1391,10 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype.arc = function(params) {
|
||||
Drone.extend('arc',function(params) {
|
||||
params.drone = this;
|
||||
_arc2(params);
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
// ========================================================================
|
||||
// Private variables and functions
|
||||
// ========================================================================
|
||||
|
|
@ -1487,10 +1585,10 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
_fisherYates(blockDistribution);
|
||||
return blockDistribution;
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.rand = function(dist,w,h,d){
|
||||
Drone.extend('rand',function(dist,w,h,d){
|
||||
var randomized = _rand(dist);
|
||||
return this.boxa(randomized,w,h,d);
|
||||
};
|
||||
this.boxa(randomized,w,h,d);
|
||||
});
|
||||
var _trees = {
|
||||
oak: org.bukkit.TreeType.BIG_TREE ,
|
||||
birch: org.bukkit.TreeType.BIRCH ,
|
||||
|
|
@ -1499,16 +1597,22 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
};
|
||||
for (var p in _trees)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Drone.prototype[p] = function(v){
|
||||
return function(){
|
||||
Drone.extend(p, function(v) {
|
||||
return function() {
|
||||
var block = this.world.getBlockAt(this.x,this.y,this.z);
|
||||
if (block.typeId == 2){
|
||||
this.up();
|
||||
}
|
||||
var treeLoc = new org.bukkit.Location(this.world,this.x,this.y,this.z);
|
||||
var successful = treeLoc.world.generateTree(treeLoc,v);
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
if (block.typeId == 2){
|
||||
this.down();
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
}(_trees[p]);
|
||||
}(_trees[p]));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype.garden = function(w,d)
|
||||
Drone.extend('garden',function(w,d)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// make sure grass is present first
|
||||
this.down().box(2,w,1,d).up();
|
||||
|
|
@ -1521,12 +1625,12 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
};
|
||||
|
||||
return this.rand(dist,w,1,d);
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Drone's clipboard
|
||||
//
|
||||
Drone.clipBoard = {};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.copy = function(name, w, h, d)
|
||||
Drone.extend('copy', function(name, w, h, d)
|
||||
{
|
||||
var that = this;
|
||||
var ccContent = [];
|
||||
|
|
@ -1541,10 +1645,9 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.clipBoard[name] = {dir: this.dir, blocks: ccContent};
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
Drone.prototype.paste = function(name)
|
||||
Drone.extend('paste',function(name)
|
||||
{
|
||||
var ccContent = Drone.clipBoard[name];
|
||||
var srcBlocks = ccContent.blocks;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1624,10 +1727,9 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
};
|
||||
Drone.prototype.cylinder0 = _cylinder0;
|
||||
Drone.prototype.cylinder = _cylinder1;
|
||||
});
|
||||
Drone.extend('cylinder0',_cylinder0);
|
||||
Drone.extend('cylinder', _cylinder1);
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
// make all Drone's methods available also as standalone functions
|
||||
|
|
@ -1638,6 +1740,7 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
//
|
||||
// ... which is a short-hand way to create a wooden building 7x3x4
|
||||
//
|
||||
/*
|
||||
var ops = ['up','down','left','right','fwd','back','turn',
|
||||
'chkpt','move',
|
||||
'box','box0','boxa','prism','prism0','cylinder','cylinder0','arc',
|
||||
|
|
@ -1655,9 +1758,10 @@ Used when placing torches so that they face towards the drone.
|
|||
};
|
||||
}(ops[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
//
|
||||
// wph 20130130 - make this a method - extensions can use it.
|
||||
//
|
||||
Drone.prototype._getBlockIdAndMeta = _getBlockIdAndMeta;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}());
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Reference in a new issue